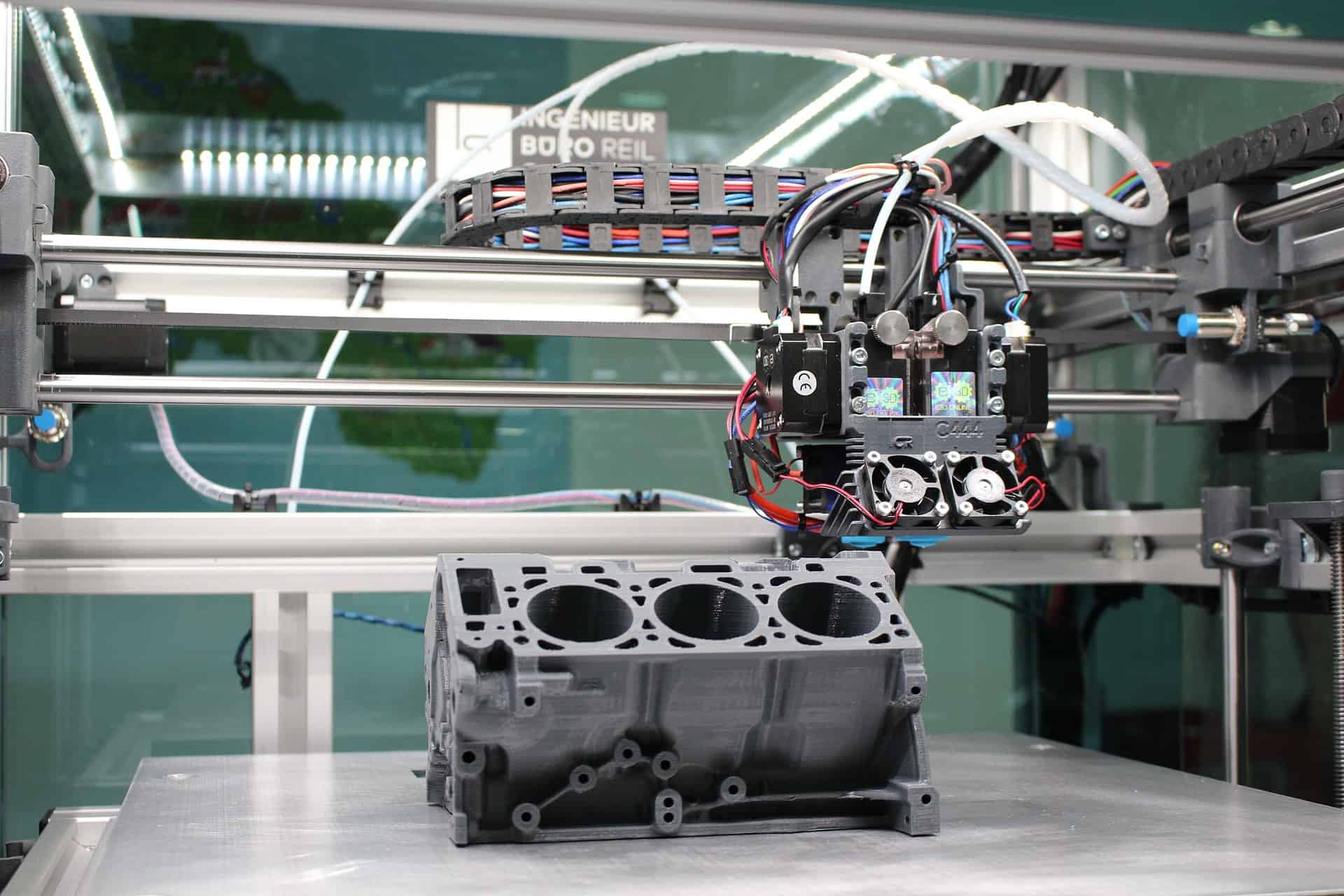
JAKARTA, odishanewsinsight.com – My first encounter with additive manufacturing was, well, messy. Picture a 3D printer in my living room, random filaments scattered everywhere, and a lopsided prototype of a phone holder. I learned real quick: it’s not just about pressing ‘print’. You’ve gotta understand materials, temperature, and software quirks.
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, is a transformative technology that is revolutionizing the way we design and produce complex structures. By creating objects layer by layer, additive manufacturing allows for unprecedented levels of customization, efficiency, and innovation across various industries. In this real-world guide, I will share my insights into additive manufacturing, exploring its processes, applications, benefits, challenges, and future potential.
What is Additive Manufacturing?
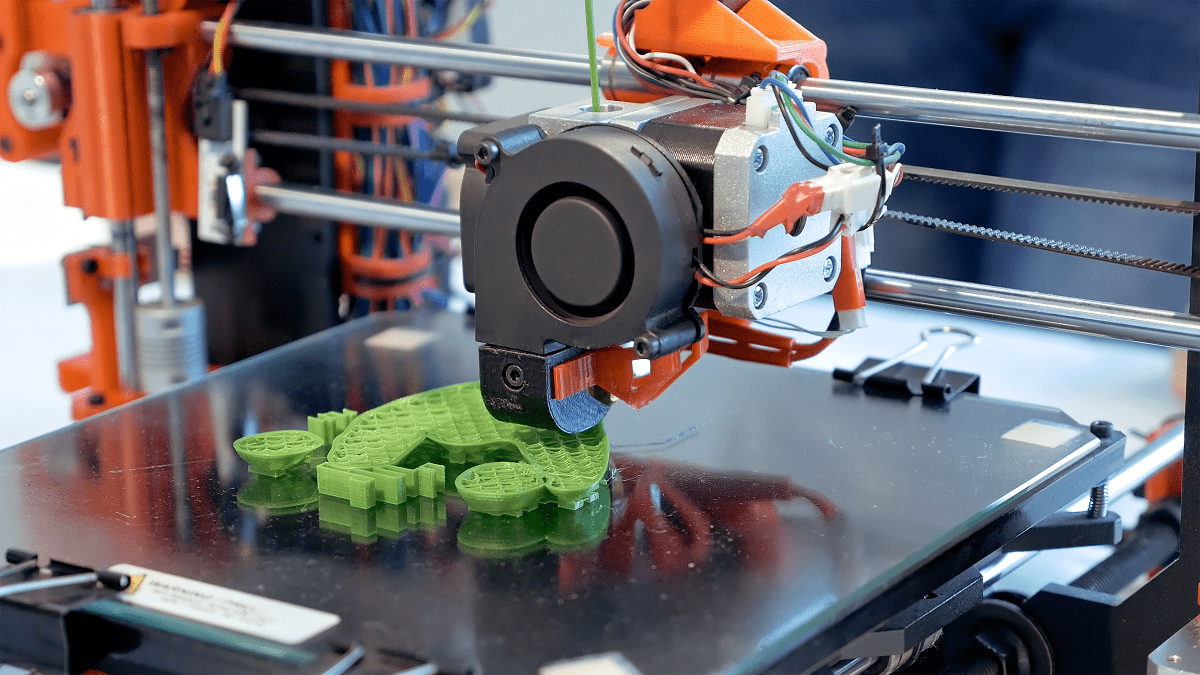
Additive manufacturing refers to a group of processes that create objects by adding material layer by layer, as opposed to traditional subtractive manufacturing methods, which involve cutting away material from a solid block. This layer-by-layer approach enables the creation of intricate geometries and complex designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with conventional manufacturing techniques.
Key Processes in Additive Manufacturing
There are several primary processes used in additive manufacturing, including:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): This widely used technique involves extruding melted thermoplastic filament through a nozzle, which deposits the material layer by layer. FDM is popular for prototyping and producing functional parts due to its affordability and ease of use.
- Stereolithography (SLA): SLA employs a ultraviolet laser to solidify liquid resin one layer at a time, yielding high-resolution parts with exceptionally smooth finishes—perfect for detailed prototypes and complex geometries.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): uses a focused laser to fuse powdered materials—often nylon or metal—one layer at a time. This technique yields durable, functional components and is widely employed in aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
- Binder Jetting: In this process, a binding agent is selectively deposited onto a powder bed to create layers. After printing, the object is cured in an oven. Binder jetting is versatile and can work with various materials, including metals and ceramics.
- Directed Energy Deposition (DED): DED involves melting materials as they are deposited, typically using a laser or electron beam. This method is often used for repairing or adding material to existing components.
Applications
Additive manufacturing has found applications across a wide range of industries, including:
- Aerospace: The aerospace industry utilizes additive manufacturing to produce lightweight, complex parts that reduce fuel consumption and enhance performance. Components such as engine parts, brackets, and custom tools can be manufactured efficiently.
- Medical: In the medical field, additive manufacturing is used to create custom implants, prosthetics, and anatomical models for surgical planning. Patient-specific solutions improve outcomes and enhance the quality of care.
- Automotive: The automotive industry employs additive manufacturing for prototyping, tooling, and producing lightweight components. This technology allows for rapid design iterations and reduced lead times.
- Architecture and Construction: Additive manufacturing is being explored in architecture for creating complex building components and even entire structures. 3D-printed homes and structures can be built more quickly and sustainably.
- Consumer Products: From custom jewelry to personalized gadgets, additive manufacturing enables the production of unique consumer products tailored to individual preferences.
Benefits
Additive manufacturing offers several significant advantages:
- Design Flexibility: The ability to create complex geometries allows designers to innovate and optimize products in ways that traditional manufacturing cannot.
- Reduced Material Waste: Since additive manufacturing builds objects layer by layer, it minimizes material waste compared to subtractive methods, making it a more sustainable option.
- Customization: Additive manufacturing enables the production of customized parts and products tailored to specific requirements, enhancing user satisfaction.
- Faster Prototyping: Rapid prototyping capabilities allow for quicker design iterations, reducing time-to-market for new products.
- Supply Chain Efficiency: Additive manufacturing can streamline supply chains by enabling localized production, reducing transportation costs, and decreasing reliance on large inventories.
Challenges
Despite its numerous benefits, additive manufacturing also faces several challenges:
- Material Limitations: While the range of materials for additive manufacturing is expanding, certain applications still require materials with specific properties that may not be readily available.
- Surface Finish and Tolerance: Achieving the desired surface finish and dimensional accuracy can be challenging, particularly for certain processes like FDM. Post-processing may be required to meet specifications.
- Production Speed: While additive manufacturing is excellent for prototyping, production speed can be slower than traditional mass manufacturing methods for large-scale production.
- Regulatory Hurdles: In industries like aerospace and medical, regulatory approvals for additive-manufactured parts can be complex and time-consuming.
- Cost Considerations: Initial setup costs for additive manufacturing equipment can be high, and the economics of production must be carefully evaluated for each application.
The Future of Additive Manufacturing
The future of additive manufacturing is promising, with ongoing advancements in technology and materials. Key trends to watch include:
- Material Innovation: Continued research into new materials will expand the applications of additive manufacturing, including biocompatible materials for medical use and high-performance alloys for aerospace.
- Integration with AI and Machine Learning: The integration of AI and machine learning can optimize design processes, improve quality control, and enhance production efficiency.
- Sustainability Focus: As sustainability becomes increasingly important, additive manufacturing will play a role in reducing waste and enabling more sustainable production methods.
- Mass Customization: The ability to produce customized products at scale will become more prevalent, allowing businesses to meet the unique needs of consumers.
Conclusion
Additive manufacturing is a revolutionary technology that is reshaping industries by enabling the creation of complex structures layer by layer. With its numerous applications, benefits, and potential for future advancements, additive manufacturing is poised to play a crucial role in the next wave of industrial innovation. As we continue to explore and expand the capabilities of this technology, it is essential to address the challenges it faces and leverage its strengths to drive progress across various sectors. Whether you’re a designer, engineer, or entrepreneur, embracing additive manufacturing can open up new possibilities and transform the way we create.
Explore our “Technology” category for more insightful content!
Don't forget to check out our previous article: Digital Diplomacy: International Relations in the Cyber Sphere